Use vvctl
Command Mode
vvctl [COMMAND] runs in non-interactive mode. Common command groups include:
loginandlogout: Manage authentication. Non-interactive login honorsVV_API_TOKENorVV_EMAILandVV_PASSWORD.get,create,delete,start,stop,run,validate, andlogs: Perform day-to-day resource management.installanduninstall: Use BYOC agent helpers.config: View or edit users, servers, and contexts.
Use --help on any command or subcommand to see available flags.
Output Formats
Most get commands can format output as json, yaml, or a table. Use the --output (or -o) option to specify a format. The default format is table.
You can pipe json or yaml output to other tools for filtering. For example, to get only the RUNNING deployments from a workspace, run the following command:
vvctl get deployments --workspace migpc9aex9vi1v --o yaml | yq eval '.deployments[] | select(.latestJob.status == "RUNNING")'
Workspaces and namespaces
- Many commands require a workspace; if
--workspaceis omitted,VV_WORKSPACEis used. - Namespaces default to
VV_NAMESPACEor fall back todefault.
Example: Create a Deployment
You can create a deployment using the vvctl create deployment command. Currently, vvctl supports only JAR and Python deployments.
Creating a deployment requires an artifact URI. If you need to create and upload an artifact, use the vvctl create artifact command to obtain the required URI.
You can pass all parameters as command-line options:
$ vvctl create deployment jar \
--name vvctl-jar-deployment \
--jar-uri s3i://vvc-tenant-migpc9aex9vi1v-west-1/artifacts/namespaces/default/FlinkQuickStart-1.0-SNAPSHOT-6ba7d69116ac0be045dc7f413346815e.jar \
--main-arguments "--input /flink/usrlib/Shakespeare.txt" \
--entry-class org.example.WordCountStreaming \
--additional-dependencies s3i://vvc-tenant-migpc9aex9vi1v-eu-west-1/artifacts/namespaces/default/Shakespeare.txt
As always, you can get more information with the option --help to see what other options you can use.
Alternatively, you can define the deployment in a YAML file. Given a file named for example jar-deployment.yml:
$ cat jar-deployment.yml
---
artifact:
kind: JAR
jarArtifact:
additionalDependencies:
- s3i://vvc-tenant-migpc9aex9vi1v-eu-west-1/artifacts/namespaces/default/Shakespeare.txt
entryClass: org.example.WordCountStreaming
jarUri: s3i://vvc-tenant-migpc9aex9vi1v-west-1/artifacts/namespaces/default/FlinkQuickStart-1.0-SNAPSHOT-6ba7d69116ac0be045dc7f413346815e.jar
mainArgs: '--input /flink/usrlib/Shakespeare.txt'
name: vvctl-jar-deployment
You can create the deployment with the flag -f:
vvctl create deployment jar -f jar-deployment.yml
The YAML schema for creating a deployment is the same as the output of vvctl get deployment <id> -o yaml. You can use this command to generate a template from an existing deployment.
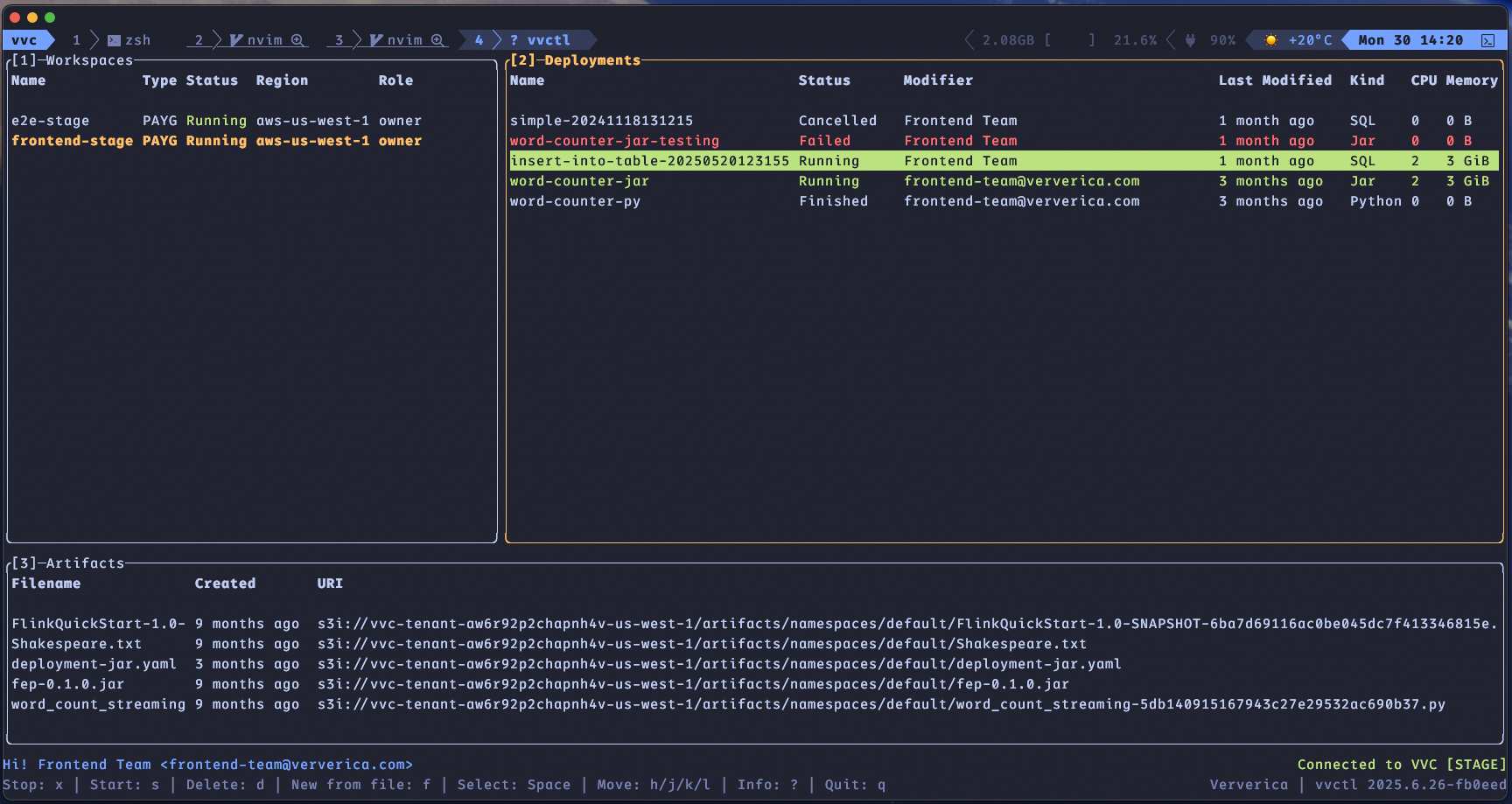
Interactive Mode
When you run vvctl without any commands, you enter an interactive mode. This Text-based User Interface (TUI) lets you manage your workspaces and deployments visually.
- Navigation: Use the arrow keys or h, j, k, and l to move.
- Selection: Press Space or Enter to select an item.
- Exit: Press q to quit the application.
The footer shows the available shortcuts for your current view.
TUI Configuration
The interactive mode reads tui.config.json, tui.config.toml, or tui.config.yaml from your vvctl configuration directory. The file is automatically created on the first run. You can use this file to adjust keybindings, colors, and refresh rates.